2018-12-23 第一周
Directory
机缘巧合,有机会可以学习这门课。问题是自己的毅力实在不足从九月份到十二月份重置了无数次,才看到第二周。今年给自己的打分绝对是1分。
From Nand to Tetris是希伯来大学的一门网络课程。选择这门课的初衷是因为毕竟从事通信行业,想要从更底层了解一下计算机。事实证明它也确实很有用,L1物理层就需要了解HDL编程。
Week1 Overview
Hello, World Below
课程目的
- 计算机如何工作
- 如何将复杂问题分解为易于管理的模块
- 如何开发大规模硬件和软件系统
向下通往硬件领地之路
任何程序在实际运行之前,首先必须被翻译成某种目标计算机平台的机器语言。其编译过程可被划分为若干个抽象层级:
- 编译器
- 虚拟机
- 汇编编译器
从概念上可分为两个阶段
- 语法分析 syntax analysis: 对源文本进行分析,分组成有意义的语言结构,保存到parse tree
- 代码生成 code generation
Boolean Logic
布尔代数 Boolean Algebra
布尔代数处理布尔型数值(true/false, 0/1 …)。
Specification
NAND
全1为0, 此课程中认为NAND是最基本的单元不需要实现
芯片名: Nand
输 入: a, b
输 出: out
功 能: If a=b=1 then out=0 else out=1
说 明: 基本门,不需实现
| a | b | Nand(a,b) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Basic Logic Gates
NOT
单输入变量的NOT gate, 也成为converter
芯片名: Not
输 入: in
输 出: out
功 能: If in=0 then out=1 else out=0
| in | out |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 |
实现:NAND(a,a)
CHIP Not {
IN in;
OUT out;
PARTS:
Nand(a = in, b = in, out = out);
}
AND
只有当输入都是1时,输出1
芯片名: And
输 入: a, b
输 出: out
功 能: If a=b=1 then out=1 else out=0
| a | b | out |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
实现:NOT(NAND(a,b)
CHIP And {
IN a, b;
OUT out;
PARTS:
// Put your code here:
Nand(a=a, b=b, out=outNand);
Not(in=outNand, out = out);
}
OR
有1为1
芯片名: Or
输 入: a, b
输 出: out
功 能: If a=b=0 then out=0 else out=1
| a | b | out |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
实现:NAND(NAND(a,a),NAND(b,b))
CHIP Or {
IN a, b;
OUT out;
PARTS:
// Put your code here:
Nand(a = a, b = a, out = aNand);
Nand(a = b, b = b, out = bNand);
Nand(a = aNand, b = bNand, out = out);
}
Xor 异或
即异或,相同为0,不同为1
芯片名: Xor
输 入: a, b
输 出: out
功 能: If a!=b then out=1 else out=0
| a | b | out |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
实现:out = not (a == b) = And(Or(a, b), Nand(a,b))
CHIP Xor {
IN a, b;
OUT out;
PARTS:
// Put your code here:
Or(a = a, b = b, out = abOr);
Nand(a = a, b = b, out = abNand);
And(a = abOr, b = abNand, out = out);
}
Multiplexor 选择器
三输入变量的门电路。
芯片名: Mux
输 入: a, b, sel
输 出: out
功 能: If sel = 0 then out=a else out=b
| a | b | sel | out |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
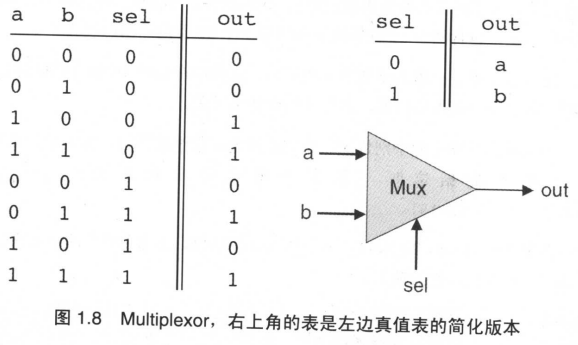
实现:[a and b] or [a and not(b) and not(c)] or [not(a) and b and c]
CHIP Mux {
IN a, b, sel;
OUT out;
PARTS:
Not(in = a , out = aNot);
Not(in = b, out = bNot);
Not(in = sel, out = selNot);
And(a = a, b = b, out = aAndb);
And(a = a, b = bNot, out = aAndnotb);
And (a = aAndnotb, b = selNot, out = aAndnotbAndnotsel);
And (a = aNot, b = b, out = notaAndb);
And (a = notaAndb, b = sel, out = notaAndbAndsel);
Or (a = aAndb, b = aAndnotbAndnotsel, out = out1);
Or(a = out1, b = notaAndbAndsel, out = out);
}
Demultiplexor
与Mux相反,只有一个输入变量,有两个输出
芯片名: DMux
输 入: in, sel
输 出: out
功 能: If sel = 0 then (a=in, b=0) else (a=0, b=in)
| in | sel | a | b |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
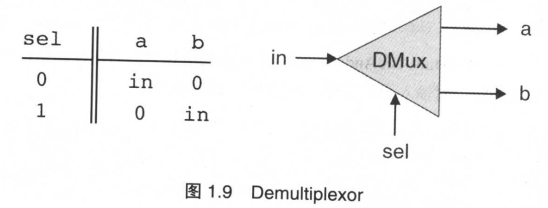
实现: a = in and not(sel), b = in and sel
CHIP DMux {
IN in, sel;
OUT a, b;
PARTS:
// Put your code here:
// a = in and not(sel)
// b = in and sel
Not(in = sel, out = notSel);
And(a = in, b = notSel, out = a);
And(a = in, b = sel, out = b);
}
Multi-Bit Versions of Basic Gates 多位基本门
通用计算机的设计要求其能够在多为数据线上运行
- Multi-Bit Not 对它的n位输入总线上的每一位取反
芯片名: Not16
输 入: in[16]
输 出: out[16]
功 能: For i=0..15 out[i]=Not(in[i])
- Multi-Bit And And16.hdl
16-bit bitwise And:
for i = 0..15: out[i] = (a[i] and b[i])
Multi-Way Versions of Basic Gates 多通道逻辑门
即将2位逻辑门推广到多位
Multi-Way Or
对于一个n位的Or门, 当n位输入变量中任意一位或以上为1,输出为1,否则为0
8-way Or:
out = (in[0] or in[1] or … or in[7])
Multi-Way/Multi-Bit Multiplexor
一个拥有m个通道,每个通道数据宽度为n位的multiplexor选择器
4-way 16-bit multiplexor:
out = a if sel == 00
b if sel == 01
c if sel == 10
d if sel == 11
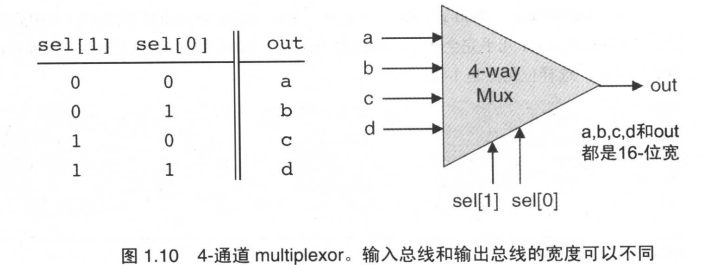
实现:机器语言是从低位到高位处理的 因此 Mux4Way16.hdl
-
Mux16(a=a, b=b, sel=sel[0], out=aa);
-
Mux16(a=c, b=d, sel=sel[0], out=bb);
-
Mux16(a=aa, b=bb, sel=sel[1], out=out);
Multi-Way/Multi-Bit Demultiplexor
m通道n位的demultiplexor从m个可能的n位输出通道中选择输出一个n位的输入变量
4-way demultiplexor:
{a, b, c, d} = {in, 0, 0, 0} if sel == 00
{0, in, 0, 0} if sel == 01
{0, 0, in, 0} if sel == 10
{0, 0, 0, in} if sel == 11

实现:太费脑子了 想不明白 怎么想出来的: 就是看哪一位有1
-
DMux(in=in, sel=sel[1], a=aa, b=bb);
-
DMux(in=aa, sel=sel[0], a=a, b=b);
-
DMux(in=bb, sel=sel[0], a=a, b=b);
下一篇 2018年过去了