Again
Directory
上一次学习这个课程是在2014-08-15左右,刚研究生的时候,现在我已经快要研究生毕业了,说实话,这两年除了年纪长了之外没有什么长进,想想也是可悲。上一次没有坚持到最后,这次要加油。
现在学习课程材料真的超级齐全。
Introduce
What is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning 的定义:
- Arthur Samuel:Field of study that give computers the ability to learn without being explicity programed.
- Mitchell :A computer program is said to learn from experience E with respect to some class of tasks T and performance measure P, if its performance at tasks in T, as measured by P, improves with experience E.
机器学习可以视为解决两个问题
- supervised learning,
- unsupervised learning.
Supervised learning
监督性学习就是使用带有标签的数据集来学习。监督性学习问题可以被分为 “regression”(回归) 和 “classification”(分类)两种。
回归问题是指预测的结果是连续的输出。分类问题预测的结果是不连续的。
Unsupervised Learning
非监督性学习是指不知道结果的情况下探索数据的结构性质或是相似性(即不包含label信息)。非监督性学习问题严格上说没有结果来比较。比如聚类问题(Clustering),鸡尾酒会问题(Cocktail Party Problem)。
Linear Regression with One Variable
一个变量的线性回归算法也称为univariate linear regression。只含有一个特征/输入变量来预测一个单独的输出。
hypothesis function:
Cost Function
也称为平方误差(Squared error function),平均平方误差(Mean squared error),使用损失函数来衡量预测函数的正确率。
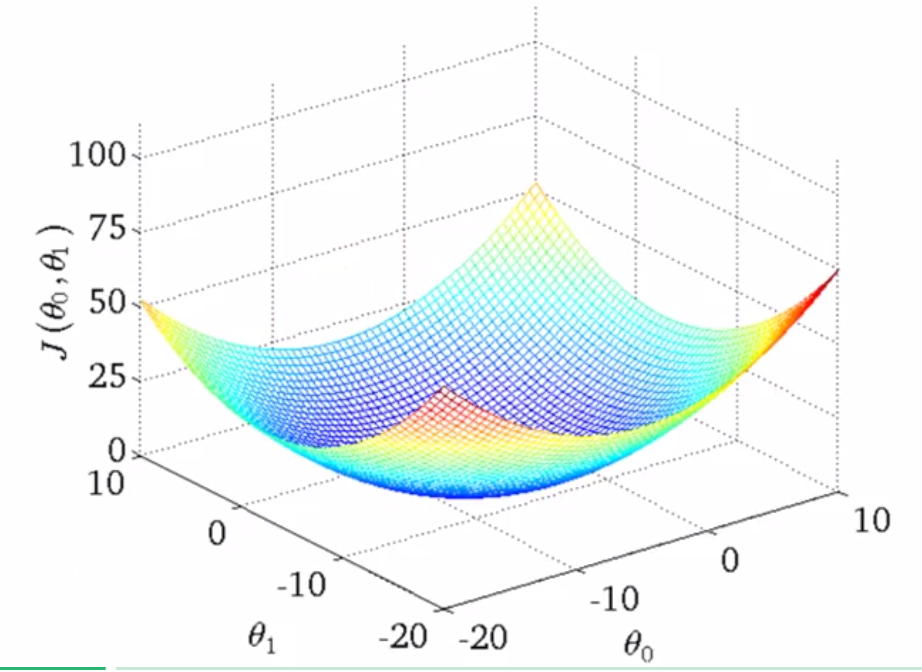
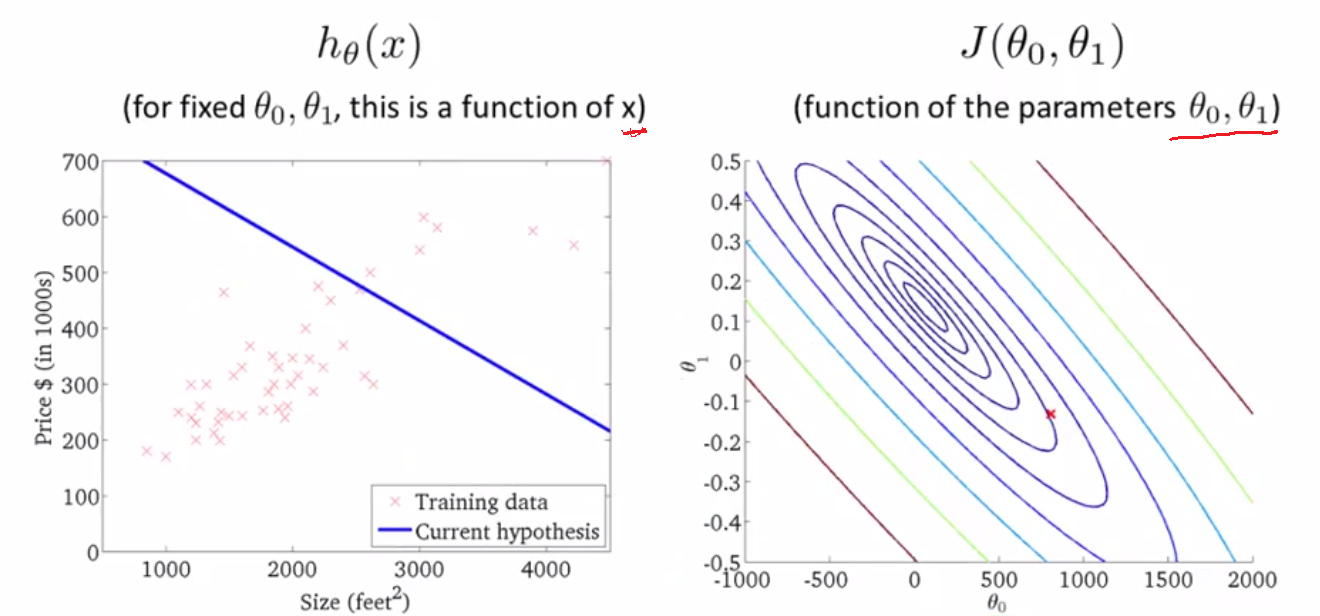
我们的目标就是找出使得误差最小的函数。
Gradient Descent
梯度下降是一个用来求函数最小值的算法。
Multiple features (variables) 多个变量的情况,介绍Gradient descent 中的 Feature Scaling, Learning rate
Normal equation Method to solve for theta analytically.
比较 Gradient Descent 和 Normal Equation ,
介绍Octave基本功能
vectorized implementation
Programming Exercises 1
2 Linear regression with one variable 2.2 Gradient Descent 2.2.3 Computing the cost J(θ)
J = (1 / (2 * m)) * sum(((X * theta - y).^2))
2.2.4 Gradient descent
% 1st
theta = theta - alpha * ( 1 / m) * (X' * (X * theta - y));
% 2nd
%temp1 = theta(1) - alpha * ( 1 / m) * sum(X * theta - y);
%temp2 = theta(2) - alpha * ( 1 / m) * sum((X(:,2) .* (X * theta - y)));
%theta = [temp1;temp2];
<div class="post-header-container>
<div class="scrim ">
<header class="post-header">
<h1 class="title">Andrew Ng 的 机器学习课程</h1>
<p class="info">by <strong>L</strong></p>
</header>
</div>
</div>
3 Linear regression with multiple variables 3.1 Feature Normalization
mu = mean(X);
sigma = std(X);
% problem: need for many other case
[m n] = size(X);
for i = 1:n
X_norm(:,i) = (X(:,i) - mu(i)) / sigma(i);
end
3.2 Gradient Descent
[plain] view plain copy
J = (1 / (2 * m)) * sum(((X * theta - y).^2));
[plain] view plain copy
theta = theta - alpha * ( 1 / m) * (X’ * (X * theta - y));
3.3 Normal Equations
[plain] view plain copy
theta = pinv(X’ * X) * X’ * y;
上一篇 Leetcode
下一篇 MathJax在blog上的应用